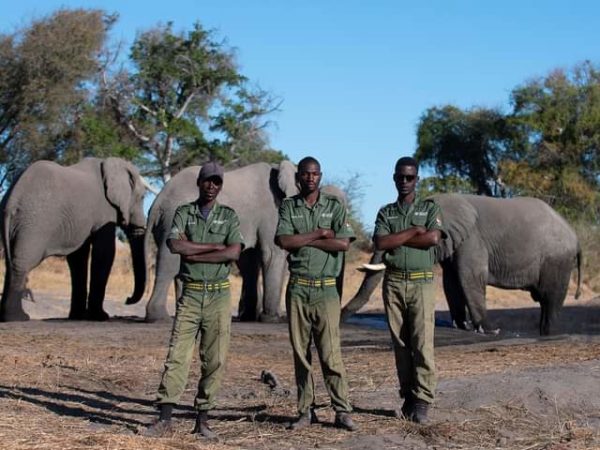
Computer Scientist, Joel Kangootui (29) grew up in a cattle post setting learning the craft of tendering for cattle at a young age. Kangootui comes from Ovaherero tribe who are revered pastoralists residing in northern Botswana.
Kangootui told The Okavango Express: ‘’ I grew up in a cattle rearing family. Our cattlepost post is located in an area teeming with wildlife. Growing up my community prioritised cattle more than wildlife. Wild Animals were considered as Government property. So to save our cattle farmers killed wild animals for meat a practice that is common this side of Botswana.’’
Kangootui admits he has also participated in bush meat trade defined as meat of wild animals killed for food. ‘’ like many other farmers in the past I used to participate in illegal hunting of wildlife like Impalas to eat. To save our cattle we would kill wild animals for meat.
Fast forward to today, Kangootui is now a fully dedicated conservationist empowering his community to desist from bush meat hunting.’’ Kangootui is taking part in the Sustainable Wildlife Management (SWIM) programme being implemented in Habu.
The project was funded by Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in collaboration with Wild Entrust Africa (WEA.) This community herding and kraaling, and ecological monitoring project is aimed at addressing some of the drivers of illegal bushmeat hunting including poverty and unemployment.
Kangootui’s role in the project include supervising community escort guides and operating the Spartial Monitoring and Reporting computer software used to study and analyse wildlife movements in Habu to come up with interventions to avoid human and wildlife conflicts and poaching.
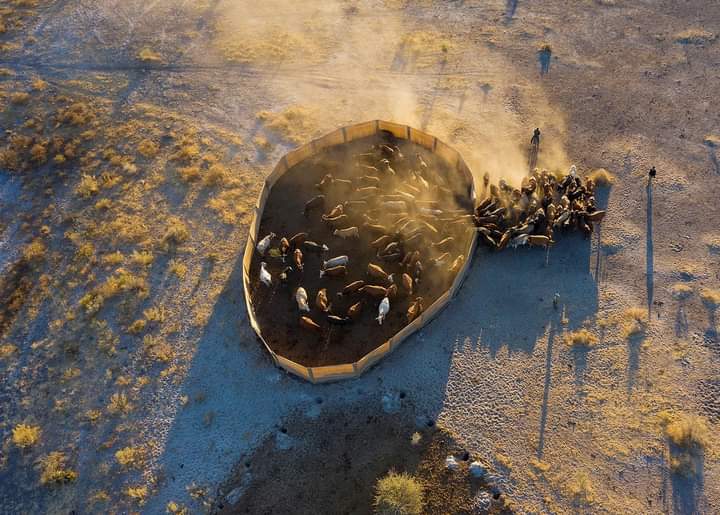
Surveys carried out have demonstrated that illegal bushmeat harvest around the Okavango Delta is substantial with an estimated 2000 hunters collecting roughly 620,000kg of bushmeat a year.
Ben Heermans, Habu project coordinator explained: ‘’at this rate illegal bushmeat undoubtedly contribute to population declines we have been seeing with some of the iconic species of the Delta. Bushmeat threaten the sustainability of the tourism industry which contributes to ~13% to Botswana’s Gross Domestic Product.’’
Heermans stated that the Swim project targets to reduce pressure on wild species that are unsustainably hunted. By working together with communities, the project identify suitable alternatives to game meat and domestic sources of protein from domestic livestock. The project is supporting the Habu community in setting up these alternative systems, both for their own consumption and for commercial purposes.
‘’With the funding we have been able to increase our staff to 40 employees, most of which are community scouts that have dual responsibilities of wildlife monitoring and human wildlife conflict mitigation through herding and kraaling of livestock.’’
Heermans explained that some of their strongest team members in wildlife monitoring efforts are the scout leaders that used to partake in bushmeat harvesting and retaliatory shootings of predators.
‘’Today these guys have put their traditional knowledge to good use and have been helpful in tracking illegal hunter movements and deter predator movements away from our livestock program.’’
Heermans further stated that the project aim to establish consistent alternative protein supplies to bush meat and assist farmers with access to markets through wildlife friendly beef branding schemes and accessing new commodity-based beef markets that take advantage of new FMD control measures that do not require the geographical separation of wildlife and livestock. ‘’
‘’We are on the verge of trialling our first wildlife-friendly compliant slaughter herd through introduction of mobile quarantine to quarantine cattle on site.
‘’To really have an impact on the bushmeat trade it is important that alternative revenue streams are developed. Some of our attempts to increase the benefits that wildlife based economies can bring to western Ngamiland’’ he said.
Habu Village Chief Mod Masedi told The Okavango Express that Habu Community Trust awaits for permission to run tourism operations in the region. Applications to run tourism camps were submitted in 2018 and are still pending. Masedi said this non-consumptive utilization of resources has garnered community support for more sustainable natural resource utilization

